6/9/2021
This new blog series is designed to illustrate the advantages of Group Assisted Purification Peptide Synthesis (GAP-PS) from GAP Peptides, based on the five foundational principles of our philosophy. Those principles are Scalability, Efficiency, Economy, Quality, and Green Chemistry. One of the easiest ways to do this is by highlighting peer-reviewed papers applicable to these topics. The first and second entries in the series covered Green Chemistry and Scalability. They, and future ones, can be accessed here.
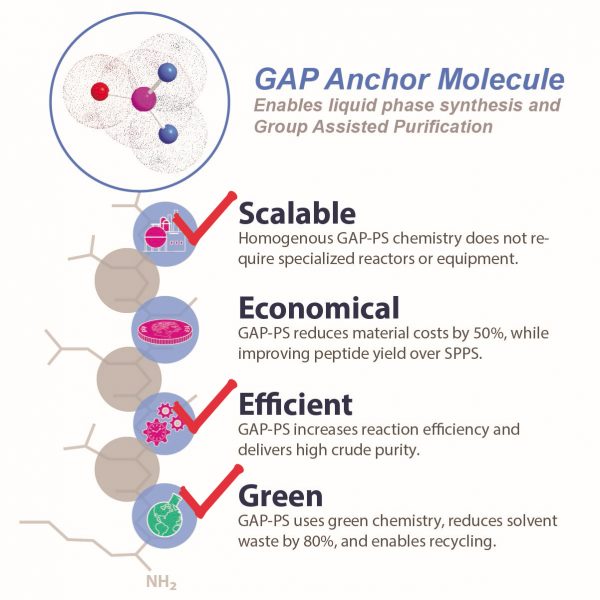
Efficiency – and by extension, the topic of our next entry – economy, is vitally important to make the process of green chemistry peptide synthesis viable. Herewith, papers that address this point are examined. Generally, efficiency is exhibited by a decrease in the overall effort necessary to achieve the desired outcome. Of course, it is the ratio of effort. It is possible to increase the desired outcome metric as well.
The first paper deals with both of these approaches, with a “GAP protecting group replacing a polymer support, facilitating C→N Fmoc peptide synthesis without chromatography or recrystallization.”1 The authors report, “over 1 gram of the immunostimulant, thymopentin, was synthesized in high overall yield (83 %) and purity (99 %).”1 Therefore the efficiency is achieved by the reduction of steps and the high yield and purity.
The second example is taken from the book, Peptide Therapeutics: Strategy and Tactics for Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Controls. The authors of the cited chapter, Rodney Lax and Trishul Shah, guide the reader through the economies and sustainability of peptide therapeutics, including the issues contract manufacturing organizations (CMOs) face. They also explain the market of peptide therapeutics, trends, and the main commercial manufacturing methods. Group Assisted Purification Peptides Synthesis is mentioned as an efficient option to traditional methodologies, specifically for CMOs. It makes for fascinating reading and is recommended as a guide for navigating current and future challenges.2
GAP-PS coupling reactions are most often run with only 10% excess amino acids (1.1 eq.) and coupling reagents. The coupling efficiency results in high crude purity by reducing or eliminating deletion sequences. The GAP anchor has a loading capacity of > 3 mmol/g, or 2-3 times the capacity for the best SPPS resins. Increased loading plus reduced solution-phase processing time allows for more product output in the same amount of reactor time, increasing throughput. SPPS can require large amounts of solvent for resin suspension, swelling and washing. GAP-PS runs near the saturation point of solvent, dramatically reducing solvent waste.
Sustainability with less expensive synthesis – what’s holding you back? Contact GAP Peptides for more information today!
References
- Cole W. Seifert, Armando Paniagua, Gabrielle A. White, Lucy Cai, Guigen Li, GAP Peptide Synthesis Through the Design of a GAP Protecting Group: An Fmoc/tBu Synthesis of Thymopentin Free From Polymers, Chromatography and Recrystallization, EurJOC, 9, 1714 (2016).
DOI: 10.1002/ejoc.201600026 - Peptide Therapeutics: Strategy and Tactics for Chemistry, Manufacturing, and Controls, Ved Srivastava (Editor) Royal Society of Chemistry, 9781788014335, 543pp. Publication Date: August 28, 2019
