6/30/2021
This blog series concludes with this entry. It is designed to illustrate the advantages of Group Assisted Purification Peptide Synthesis (GAP-PS) from GAP Peptides, based on the four foundational principles of our philosophy. Those principles are Scalability, Efficiency, Economy, and Green Chemistry. One of the easiest ways to do this is by highlighting peer-reviewed papers applicable to these topics. The previous three entries in the series covered Green Chemistry, Scalability, and Efficiency. They, and future ones, can be accessed here.
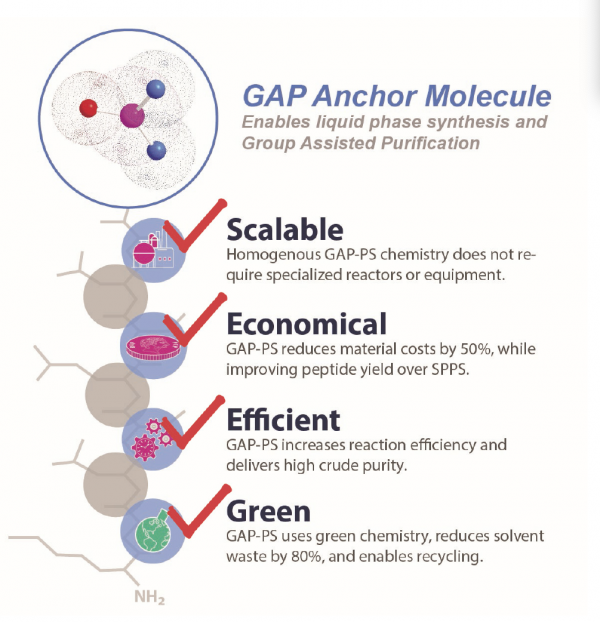
Economy, which is a consequence of our previous entry efficiency, is further examined in our fourth foundational principle. And no matter how those three previously discussed principles are (Scalability, Efficiency, and Green Chemistry), if they are not economically viable, they will not be used in a commercial setting. GAP Peptides is strongly committed the proposition that green chemistry must be economically viable in order to succeed, and as a consequence of its patented process, it clearly is!
Solvents are one of the largest cost components and the largest waste by-product of peptide synthesis. As stated by Llobet, et al., in their article, Sustainability Challenges in Peptide Synthesis and Purification: From R&D to Production, published in The Journal of Organic Chemistry, “solvents represent the vast majority of the waste generated in chemical processes, and this is especially relevant for solid-phase peptide synthesis”.2 As any lab safety manager – or peptide chemist – can attest, “DMF, NMP, and in lower amounts, dichloromethane, diethyl ether, and tert-butyl methyl ether, all present various hazards and most importantly, DMF and NMP have reproductive toxicity hazards.”2 GAP-PS eliminates the use of these hazardous solvents, and drastically cuts solvent consumption; furthermore, due to reaction efficiency, impurities are minimal and crude purity is high. Therefore, the GAP-PS approach not only creates significant economic advantages due to reduced consumption of raw material and reduced purification costs, but also enables sustainability through reuse and recycling in some cases. Additionally, this saves on purification labor too. This is all addressed by combining the advantages of solution phase and Fmoc chemistry. Coupling reactions are run in solution, near the saturation point of the solvent. Compared to SPPS, GAP-PS reduces solvent costs by more than 60%. The homogenous process also reduces raw material costs by more than 50%, and is estimated to reduce labor cost by 30 – 45%.
Whether you are a bench chemist, lab director, or in the corporate suite, the economics are the final and most persuasive case that can be made for switching to Group Assisted Purification Peptide Synthesis from GAP Peptides. Sustainability with less expensive synthesis – what’s holding you back? Contact GAP Peptides for more information today!
References
- C. W. Seifert, C.S. Brooks, Cost-Savings Potential of GAP-Peptide Synthesis https://gappeptides.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/04/Lowering-Costs-Saving-Time-Reducing-Resource-Consumption_2021.pdf
- Albert Isidro-Llobet*, Martin N. Kenworthy*, Subha Mukherjee*, Michael E. Kopach*, Katarzyna Wegner*, Fabrice Gallou*, Austin G. Smith*, and Frank Roschangar, J. Org. Chem., 84, 8, 4615 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.joc.8b03001
Further Reading
O. Al Musaimi, D. Al Shaer, B.G. De La Torre, F. Albericio, Green Circular Economy Applied To Peptide Synthesis, Chimica Oggi – Chemistry Today, 39(2),18 (2021).
